Now Reading: Silent Volcanoes: Why Some Erupt Without Warning
-
01
Silent Volcanoes: Why Some Erupt Without Warning
Silent Volcanoes: Why Some Erupt Without Warning

Rapid Summary
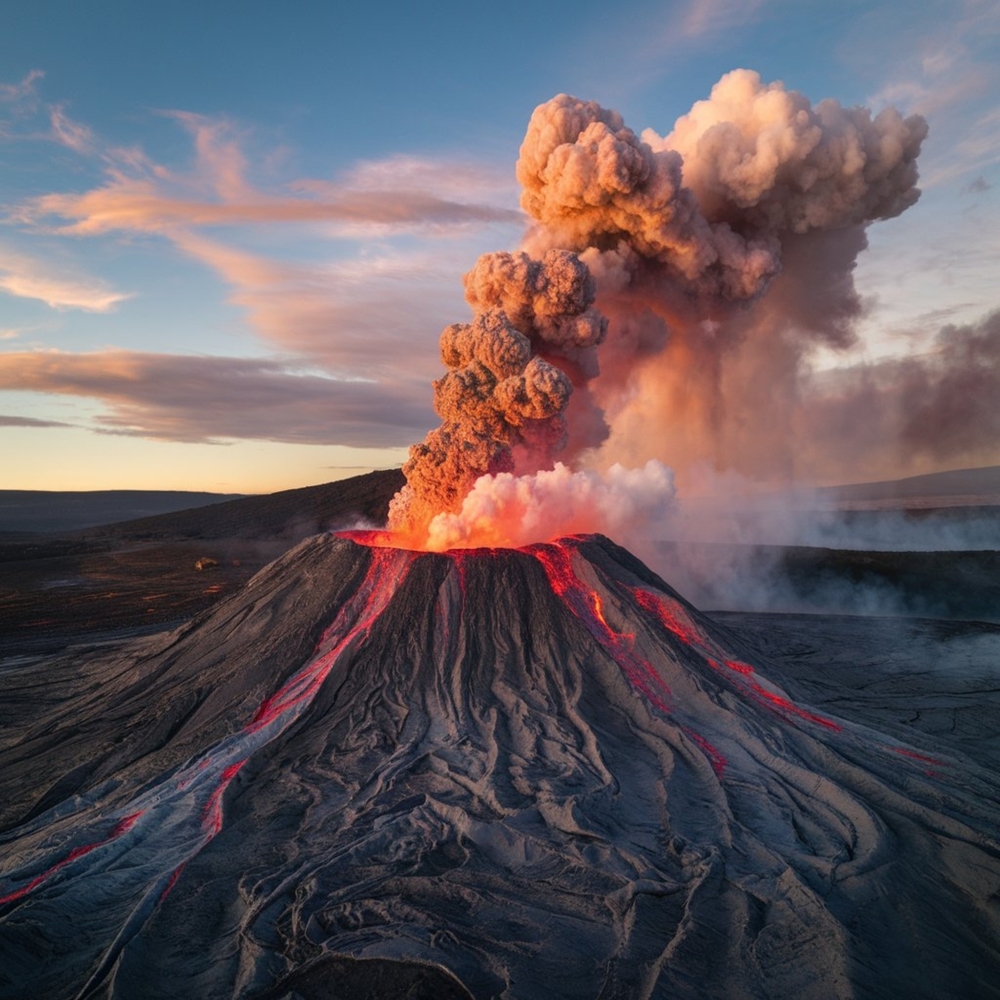
- Volcanic Eruption: In February 2021, Alaska’s mount Veniaminof erupted unexpectedly, releasing ash adn toxic gases for three days without warning signs.
- Past Events: Out of 13 eruptions at Veniaminof since 1993,only two showed typical precursory signals like seismic activity or ground deformation. These are known as “stealthy” eruptions.
- Scientific Study: Researchers from the University of Illinois used data and modeling to understand specific conditions leading to stealthy eruptions.
- Findings: Stealthy eruptions occur due to low magma flow into small chambers warmed by persistent magma presence, reducing rock failure and detectable warning signs.
- Implications for Monitoring: The study highlights the need for advanced technologies like borehole tiltmeters, fiber optic sensors, infrasound tools, gas emission monitors, and machine learning for detecting subtle volcanic changes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research on “stealthy” volcanoes has meaningful implications globally but holds unique relevance for India given its proximity to active volcanic regions such as Indonesia. India’s efforts in disaster preparedness could benefit from integrating advanced monitoring technologies highlighted in this study. While Indian volcanology largely focuses on semi-active sites like Barren Island or Narcondam in the Andaman Islands region, understanding stealth-style eruption dynamics can inform precision-based surveillance methods.Moreover, adopting machine learning-driven techniques-another key advice-aligns well with India’s broader AI development initiatives. Proactive request of these findings may strengthen India’s capacity against surprise natural disasters while bolstering regional collaboration with neighboring countries facing similar geological threats.