The tenth test flight of SpaceX Starship is scheduled for Sunday, August 24, with the launch window opening at 6:30 p.m. CT. The booster on this flight test is attempting several flight experiments to gather real-world performance data on future flight profiles and off-nominal scenarios. The Super Heavy booster will attempt these experiments while on a trajectory to an offshore landing point in the Gulf of America and will not return to the launch site for catch.
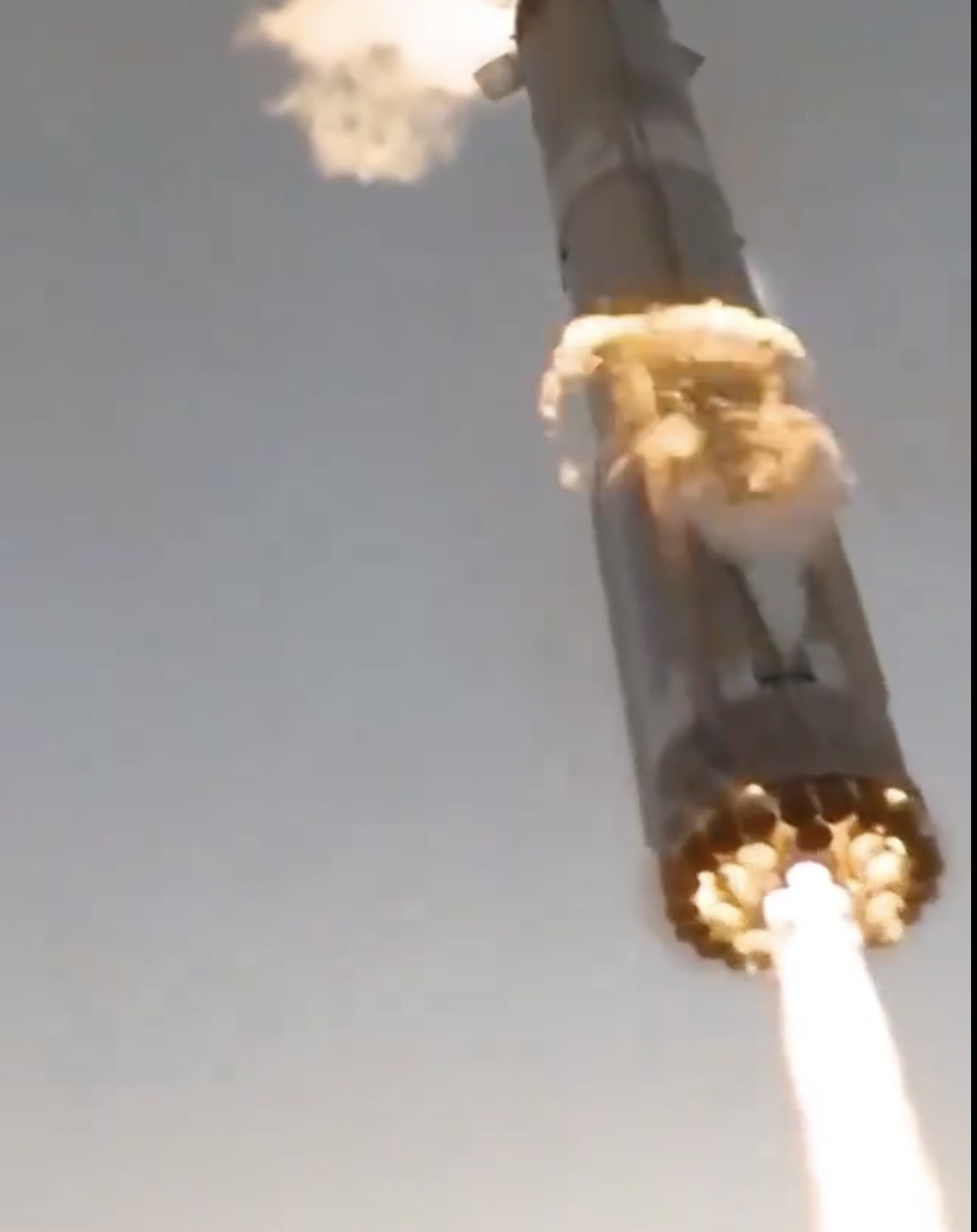
Following stage separation, the booster will flip in a controlled direction before initiating its boostback burn. This maneuver was demonstrated for the first time on Flight 9 and requires less propellant to be held in reserve, enabling the use of more propellant during ascent to enable additional payload mass to orbit.
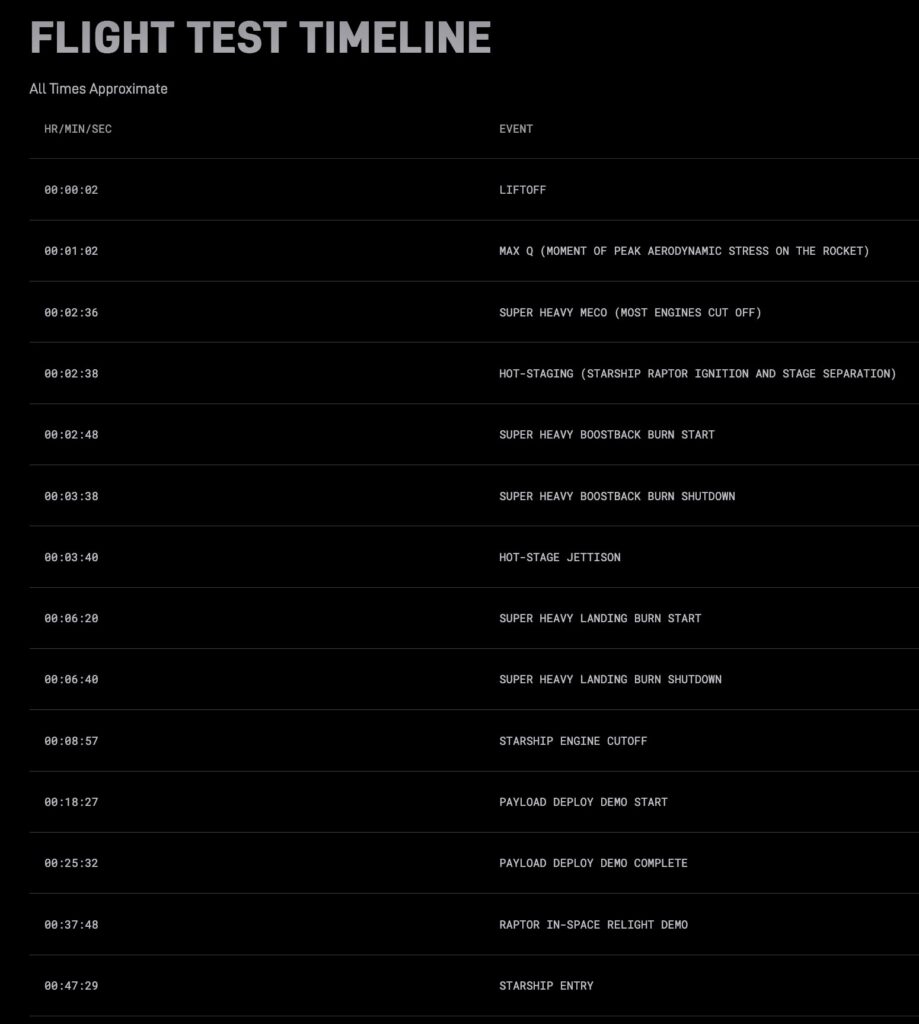
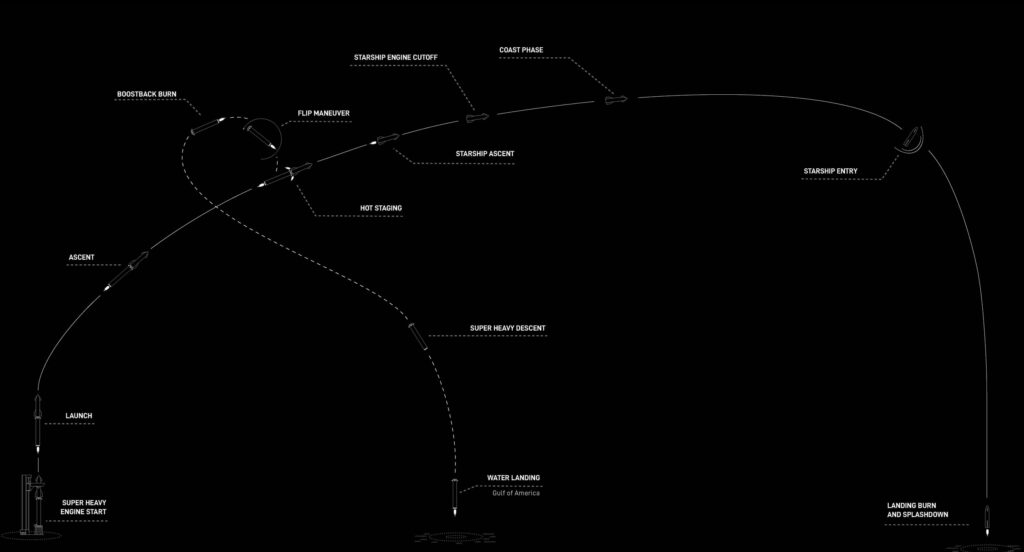
The primary test objectives for the booster will be focused on its landing burn and will use unique engine configurations. One of the three center engines used for the final phase of landing will be intentionally disabled to gather data on the ability for a backup engine from the middle ring to complete a landing burn. The booster will then transition to only two center engines for the end of the landing burn, entering a full hover while still above the ocean surface, followed by shutdown and drop into the Gulf of America.
The Starship upper stage will again target multiple in-space objectives, including the deployment of eight Starlink simulators, similar in size to next-generation Starlink satellites. The Starlink simulators will be on the same suborbital trajectory as Starship and are expected to demise upon entry. A relight of a single Raptor engine while in space is also planned.
The flight test includes several experiments focused on enabling Starship’s upper stage to return to the launch site. A significant number of tiles have been removed from Starship to stress-test vulnerable areas across the vehicle during reentry. Multiple metallic tile options, including one with active cooling, will test alternative materials for protecting Starship during reentry. On the sides of the vehicle, functional catch fittings are installed and will test the fittings’ thermal and structural performance, along with a section of the tile line receiving a smoothed and tapered edge to address hot spots observed during reentry on Starship’s sixth flight test. Starship’s reentry profile is designed to intentionally stress the structural limits of the upper stage’s rear flaps while at the point of maximum entry dynamic pressure.

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.