Now Reading: Study Confirms Adult Brains Generate New Neurons, Ending Scientific Debate
-
01
Study Confirms Adult Brains Generate New Neurons, Ending Scientific Debate
Study Confirms Adult Brains Generate New Neurons, Ending Scientific Debate
Quick Summary
- Scientists have conclusively demonstrated the presence of newly formed neurons in adult human brains,resolving a long-standing debate over whether neurogenesis occurs in adults.
- The study, published in Science, found neural precursor cells (cells capable of turning into neurons) and immature neurons in the hippocampi of human brains ranging from age 13 to 78.
- Researchers used advanced RNA sequencing techniques to identify molecular markers that indicate cell life stages. These markers were consistent across child and adult brains.
- Neural precursor cells were detected in 12 out of 19 adult postmortem brains studied, wiht some individuals showing considerably higher levels due to potential factors like epilepsy.
- The hippocampus remains the primary site for confirmed neurogenesis; other areas, such as the olfactory bulb, are still under inquiry for similar activity.
- Further research may link disrupted neurogenesis to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and depression, offering potential pathways for studying brain-related disorders.
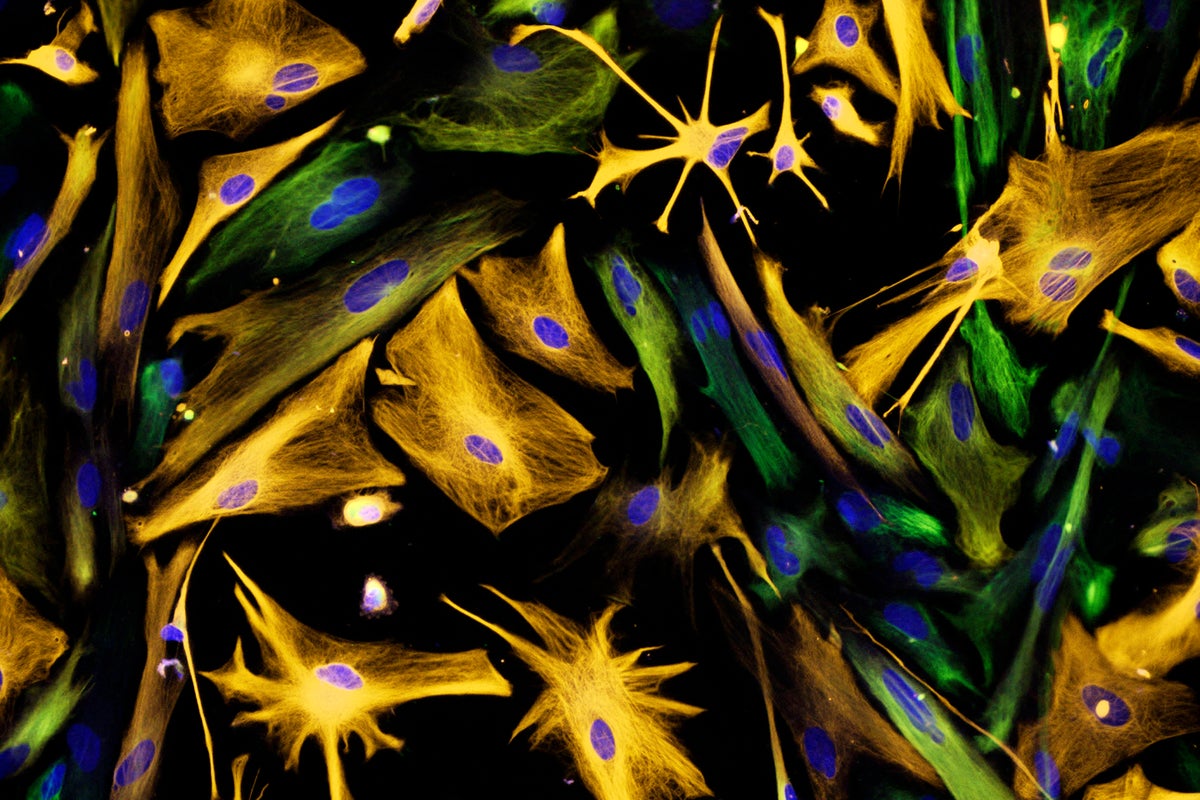
[Image: Fluorescence light micrograph depicting neural progenitor cells (green), astrocytes (orange), and nuclei (blue)]
Source: Carol N. Ibe and Eugene O. Major/National Institutes of Health/Science Source
Indian Opinion Analysis
The confirmation of adult neurogenesis by this groundbreaking study holds significant implications for neuroscience globally and could influence future medical advancements. For India-where neurological disorders like dementia are on the rise-this revelation opens avenues for deeper understanding and treatment strategies involving brain regeneration mechanisms. The identification of neural precursor cells may inspire collaborative global research partnerships aimed at mitigating diseases like Alzheimer’s or depression wich disproportionately impact aging populations.
While these findings currently rest within advanced scientific institutions abroad,india’s growing focus on biomedical research presents opportunities to integrate such knowledge through partnerships or training programs aimed at enhancing domestic capabilities.A clear understanding of how neurogenesis operates can advance therapies tailored toward memory preservation-a pressing need given India’s demographic trends toward urbanization-induced stress conditions that often exacerbate mental health challenges.
Moreover, this discovery invites ethical consideration regarding its submission in treatments or enhancements within healthcare systems fighting limited resources-underscoring that developing nations must balance innovation with accessibility.