Now Reading: Study Finds Preference for Antagonistic Leaders in Competitive Societies
-
01
Study Finds Preference for Antagonistic Leaders in Competitive Societies
Study Finds Preference for Antagonistic Leaders in Competitive Societies

Swift Summary
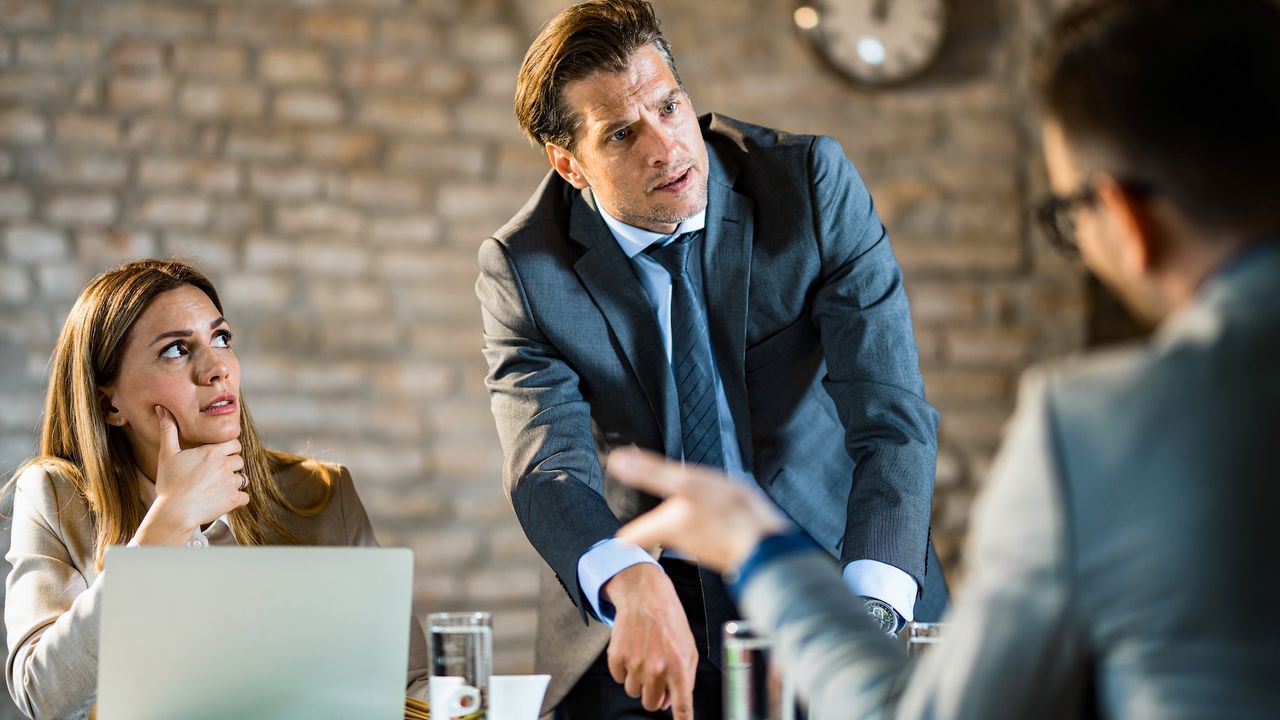
- A new study reveals that reactions to antagonistic leaders depend on an individual’s worldview.
- People who view society as competitive are more likely to admire and evaluate such leaders as competent and effective. Conversely, cooperative-minded individuals find these leaders ineffective.
- The study surveyed over 2,000 U.S.-based participants using hypothetical scenarios, workplace examples, and evaluations of real-world CEOs like Tim Cook and Bob Iger.
- Participants with “competitive jungle beliefs” were more likely to approve of coercive behaviors like making threats or blaming others in leadership roles.
- Researchers suggested that antagonistic leaders might attract employees who share competitive worldviews over time.
- The findings highlight how personal belief systems shape perceptions of leadership effectiveness.
- Even tho based on a U.S.-centric sample, researchers hope the work sparks reflection on leadership evaluations globally.
Indian opinion Analysis
This study holds relevance for India’s evolving corporate landscape where globalization has introduced diverse management practices. Indian workplaces blend traditional collaborative norms with the increasing adoption of globalized leadership styles that often prioritize competitiveness. Understanding how cultural beliefs affect leadership perception can help Indian organizations foster better leader-follower dynamics by adapting styles suited for different workforces or regions.
Additionally, debates over the meritocracy vs hierarchy-driven models within Indian politics and business could benefit from discussions this research enables-highlighting why certain authoritative figures gain public validation in contrast to those promoting inclusive approaches.
Read More: LiveScience