Now Reading: How Magellanic Penguins Navigate Ocean Currents Smartly
-
01
How Magellanic Penguins Navigate Ocean Currents Smartly
How Magellanic Penguins Navigate Ocean Currents Smartly

Quick Summary
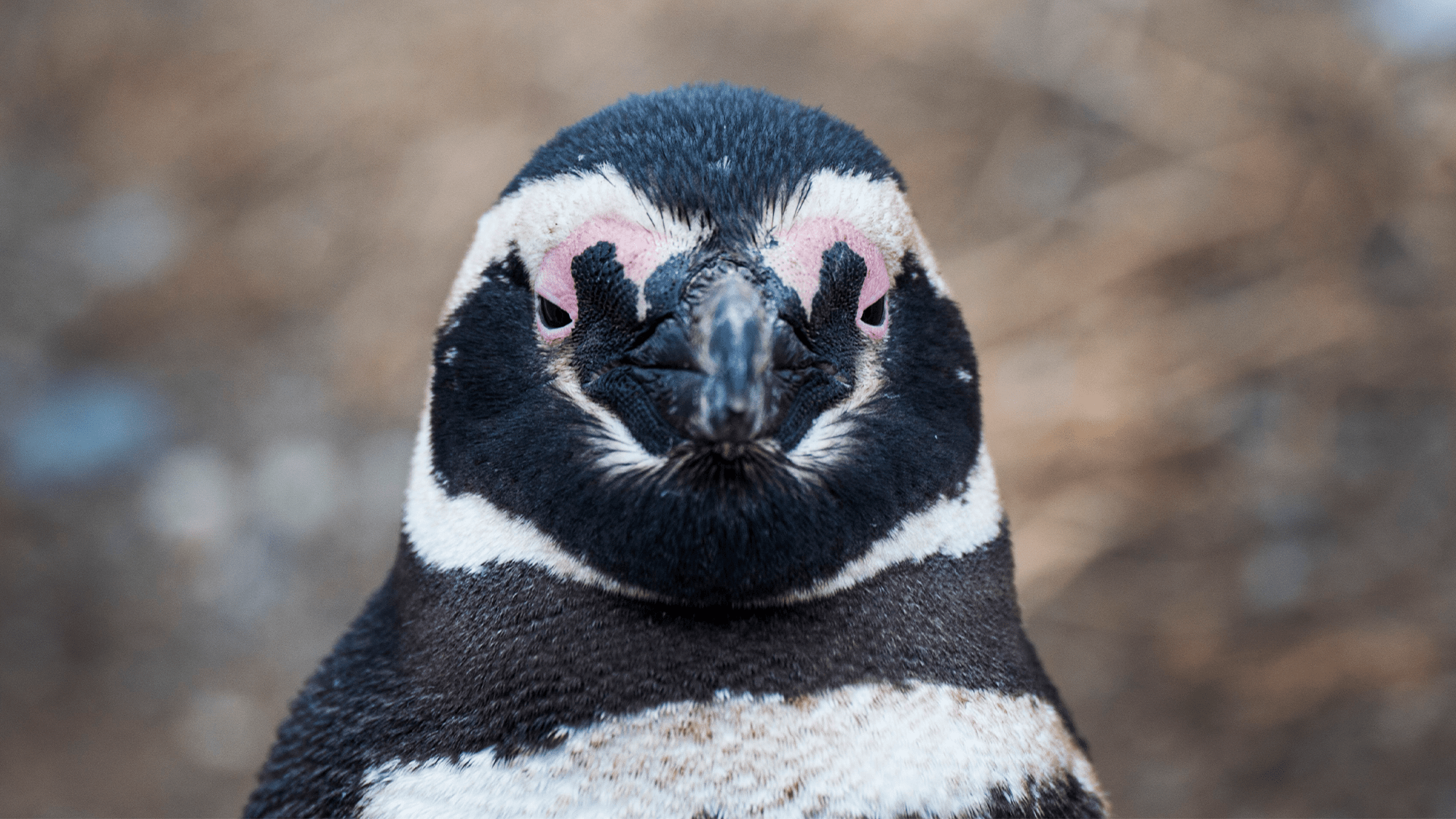
- Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) travel up to 1,200 miles during migrations and utilize tidal currents to save energy and improve navigation accuracy.
- penguins adjust their travel routes by subtly exploiting ocean currents, balancing efficiency with opportunistic foraging along the way.
- Researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior fitted 27 adult penguins in Argentina with GPS and IMU loggers to study their navigation patterns under different current conditions.
- Findings suggest that the penguins alternate between swimming directly toward destinations and drifting laterally with the flow of strong currents, saving some energy while maintaining remarkable navigational precision even in challenging conditions.
- This behavior enhances understanding of marine animal navigation strategies but requires more research across species and larger sample sizes.
!Image: Magellanic penguin on Magdalena island. CREDIT: Martin Bernetti/AFP via Getty Images.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s robust coastline fosters diverse marine habitats that could benefit from continued research into migration patterns similar to those observed in magellanic penguins. Studies like this highlight intricate adaptations by marine animals navigating vast oceans without visual landmarks-key ecological insights as India prioritizes sustainability in its maritime domain. Incorporating lessons from global studies might assist conservation efforts for indian seabirds or aquatic animals facing threats like habitat loss or changing sea currents due to climate change.
Given India’s emerging status as a hub for cross-disciplinary science-spanning biology, oceanography, and sensor technology-there is potential prospect for local institutions to replicate such methods within native species’ ecosystems. However, collaboration between nations will remain essential since this field advances primarily through data sharing beyond borders.