Now Reading: Three Years of War: Ukraine’s Forests and Livelihoods in Peril
-
01
Three Years of War: Ukraine’s Forests and Livelihoods in Peril
Three Years of War: Ukraine’s Forests and Livelihoods in Peril

Quick Summary
- The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has caused widespread destruction in Ukraine’s infrastructure, ecology, adn human lives. As February 2022, over a million have been killed or injured, nearly 6 million people displaced internally, and 5.7 million refugees have fled to neighboring European countries.
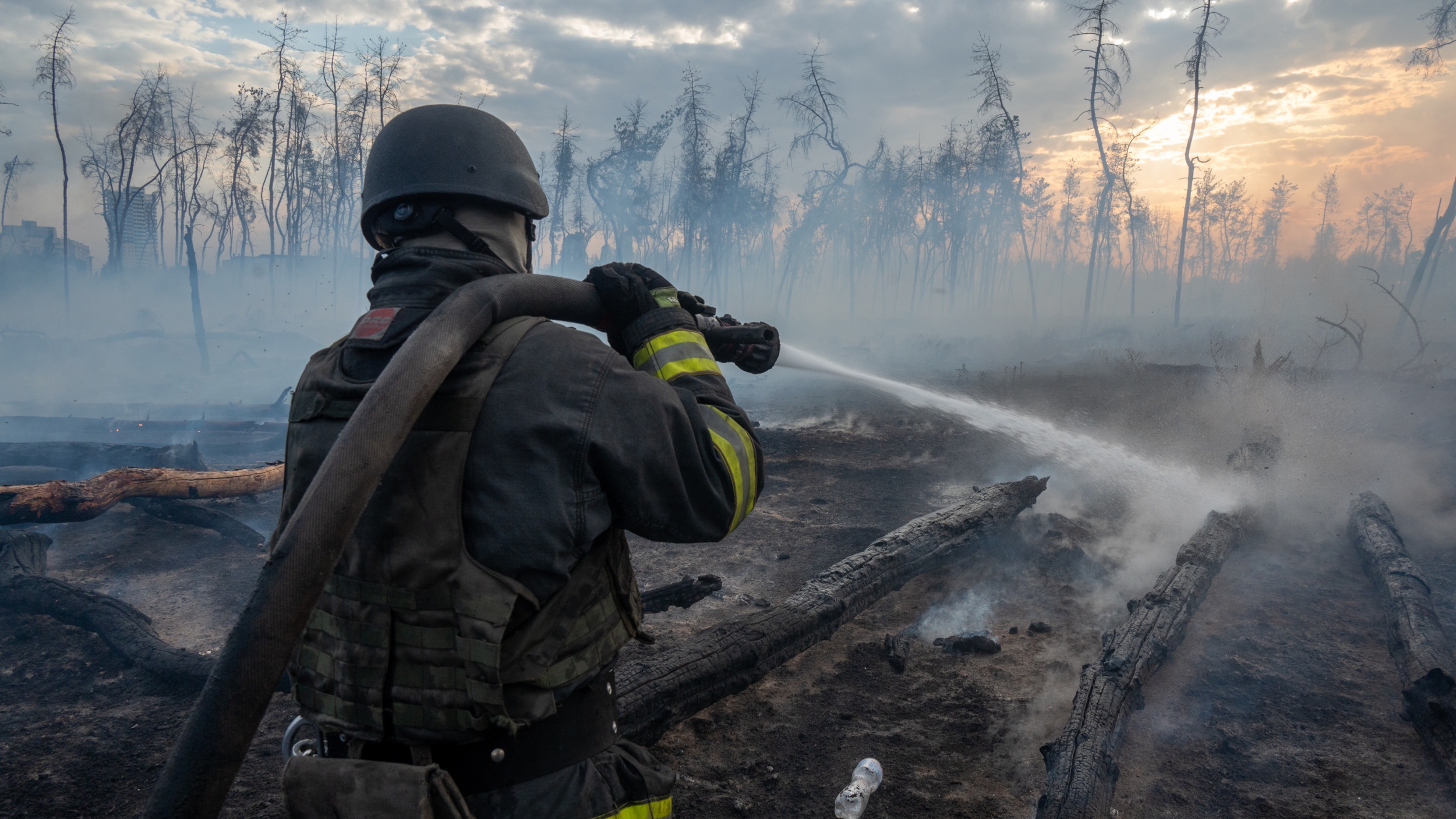
- Wildfires triggered by warfare have burned nearly 5 million acres of forested and agricultural land in Ukraine as the start of the conflict; approximately three-quarters are located within or near conflict zones.
- Warfare-related emissions now constitute over a third of ukraine’s carbon output annually, with ecosystems suffering long-term degradation due to artillery shelling and unexploded ordnance like land mines.
- Forests play a critical role in protecting Ukraine’s food supply by preventing erosion that coudl lead to drought; damage and fires threaten these forests along with their historical use as physical refuges for displaced civilians.
- Efforts from Ukrainian scientists, nonprofits like Forest Release, and AI-led demining technology aim to limit wildfire spread by mapping unexploded ordnance while training foresters for fire suppression under perilous conditions.
- International collaboration is helping advance measures like satellite monitoring systems for early detection of high-risk forests while promoting long-term reforestation strategies with less-flammable native species as part of climate-resilient restoration plans.
Images included:
- A toy truck outside a children’s cafe damaged by Russian artillery strike (Ukrinform/NurPhoto via Getty Images).
- Burning forest due to shelling in Raihorodok (Ethan Swope/Getty Images).
- Shelling scraps visible at Serebryansky forest during combat periods (pablo Miranzo/Anadolu via Getty images).
- Charred pine trees contaminated with mines seen aerially post-fire damage in Svyatohirsk area (Pierre Crom/Getty Images).
Indian Opinion Analysis
The devastation wrought on Ukraine’s natural ecosystems underscores the severe environmental impacts wars can generate alongside their social ramifications. For India-a country grappling with its own climate crises including rising wildfires-this case study highlights crucial learnings about ecosystem recovery amidst political instability.
India can observe how collaborative efforts between science communities worldwide address multi-scalar challenges such as demining hazardous zones while preserving ecological health through reforestation planning tailored to climate adaptation needs. Furthermore, advanced technologies such as AI-driven mine detection bring innovation fields applicable cross-sectorally into Indian disaster relief logistics where precision saves lives post natural calamities.
The humanitarian implications also emphasize India’s duty toward effectively preparing mechanisms fostering civilian disaster resilience; whether stemming internally-perceived displacements beyond refugee-exiegencies context globally amplifying similar vulnerabilities-to-front institutions fostering diplomatic dialogues bridging proactive remedial cooperation cross-territories limits uncertainties wherever impacting nearby entities yet resilient=.