Now Reading: Tips for Capturing Clear Microscope Specimen Photos
-
01
Tips for Capturing Clear Microscope Specimen Photos
Tips for Capturing Clear Microscope Specimen Photos

Quick Summary
- Microscope photography can be done for research, teaching or artistic purposes, and is accessible through several methods.
- Options for capturing images:
– Digital microscopes: Includes pre-installed software, SD cards, and AV/TV cables for high-resolution images and videos.
– Microscope cameras: Eyepiece tube cameras like swift’s EC5R integrate directly with monitors or computers to capture magnified images.
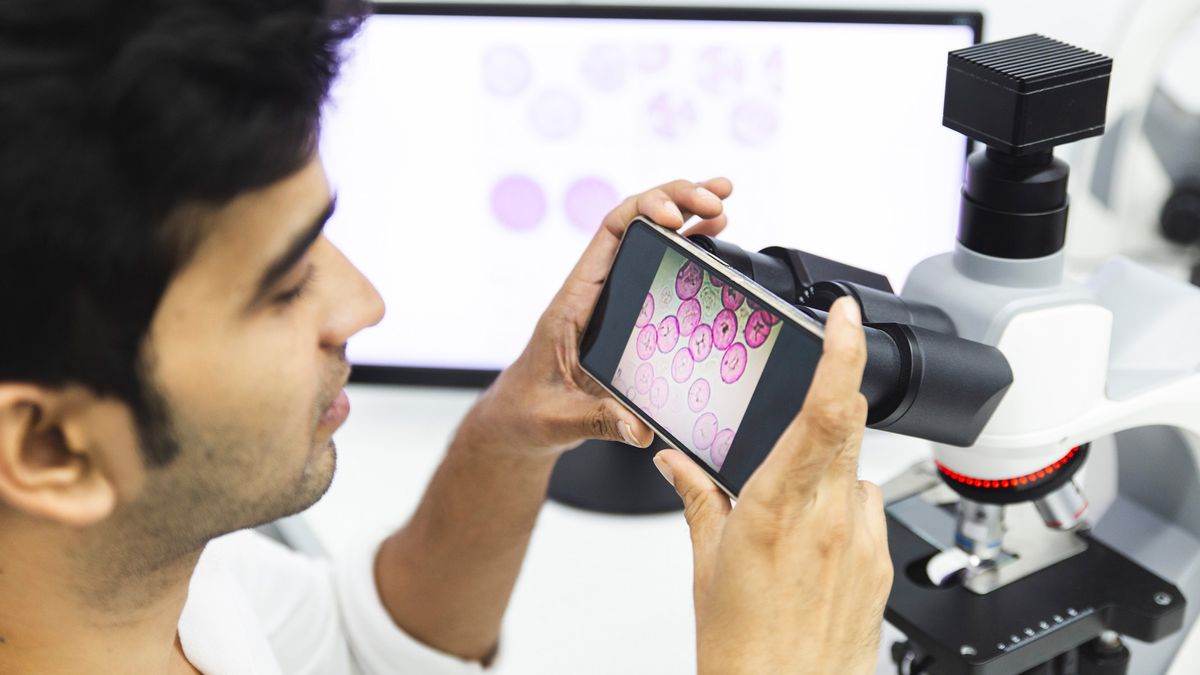
– Smartphone-based photomicrography: simple method requiring patience; using a universal smartphone mount can enhance stability.
- Professional-grade options include attaching DSLR cameras to trinocular microscopes for detailed imagery; requires compatibility between microscope and camera brands with appropriate adapters.
- Enhancements during photography:
– Colored filters improve visibility of cellular structures; ND filters optimize light intensity without altering color accuracy.
– Issues like muddy staining can be addressed using specialized filters (e.g.,didymium or ultraviolet).
- Techniques vary based on specimen type: obvious specimens (cells) require lower illumination sources while opaque ones benefit from upper lighting.Independant side spotlights aid in enhancing colors or contrast.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The detailed recommendations provided highlight the accessibility of microscale imaging techniques that could empower India’s budding researchers in biology, chemistry, materials science, and other STEM fields. Microscope photography has direct applications ranging from education in schools to professional workspaces. The availability of cost-effective methods like smartphone mounts represents an possibility for public institutions striving toward inclusive education while more advanced setups cater specifically to India’s growing cadre of scientists needing precise tools.
India’s emphasis on scientific research under government initiatives like “Atmanirbhar Bharat” aligns well with such innovations that bridge beginners’ interest with expert-level professionalism in microscopy fields. Leveraging thes technologies promotes interdisciplinary learning across environmental studies (e.g., water organism analysis), cellular imaging for medical research labs, agritech exploration in genetics/pollination-and perhaps even artistic ventures reflective uniquely disabling cost burden barriers redirect investment focus where needed!
Read more: How To Photograph Microscope Specimens