Now Reading: Top 5 Mistakes Beginners Make in Astrophotography and How to Fix Them
-
01
Top 5 Mistakes Beginners Make in Astrophotography and How to Fix Them
Top 5 Mistakes Beginners Make in Astrophotography and How to Fix Them
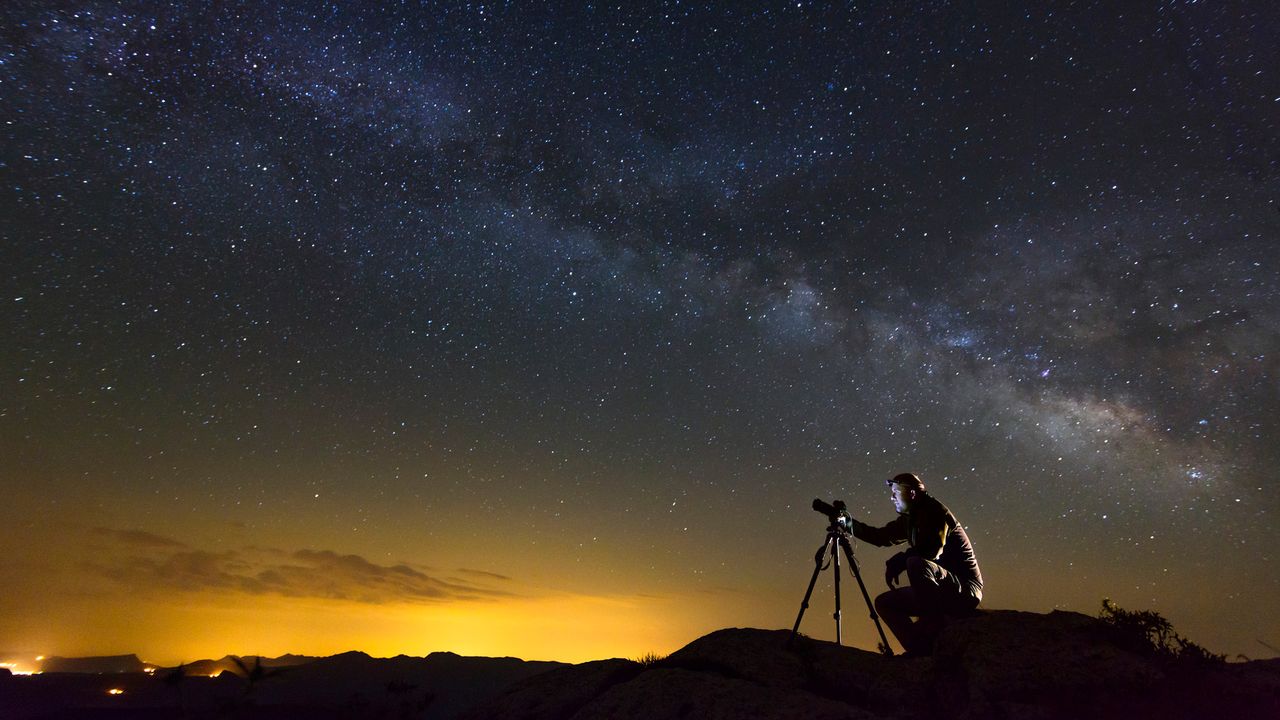

Quick summary
- Astrophotography is challenging due to the faint light and constant movement of the sky. Beginners often encounter common mistakes that can hinder capturing clear night-sky photos.
- Key mistakes include:
1. Not Nailing Focus: Precise focusing on stars is crucial for sharp images. Using features like magnified live view or Starry Sky Autofocus (on select cameras) can definitely help avoid blurry results.
2. Incorrect shutter Speed: Finding a balance between avoiding star trails and achieving sufficient brightness using the “500 rule” (or adjusted variations for camera type) is essential.3. Ignoring Sky Movement: The dynamic movement of celestial bodies requires pre-planning for composition using apps like Stellarium or PhotoPills.4. Using Excessively High ISO: Overly high ISO settings result in noisy images that lose detail, while each camera has an ideal ‘sweet spot’ for noise and brightness levels.
5.Not Shooting in RAW Format: JPEG compression discards critical details, making RAW essential for retaining image quality and editing adaptability in astrophotography.
- Practical tools such as high-quality lenses, cameras, and planning software are recommended for improving results.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The enthusiasm around advancing photography techniques resonates globally but carries unique importance in India given it’s rich heritage of celestial observation through ancient texts and astronomy traditions like Jantar Mantar observatories. With rising accessibility to digital tools such as astrophotography equipment and planning applications, these advancements allow professionals and enthusiasts alike to engage more deeply with India’s dark skies.
In India’s context, protecting night skies from increasing light pollution becomes central not just to astrophotography but also cultural preservation efforts tied to stargazing traditions across rural landscapes.Encouraging practices that blend technical education with environmental awareness might pave pathways for local photographers to merge art forms with advocacy while elevating astro-tourism prospects nationwide.