Now Reading: Unraveling India’s Stunting Crisis: Causes and Challenges
1
-
01
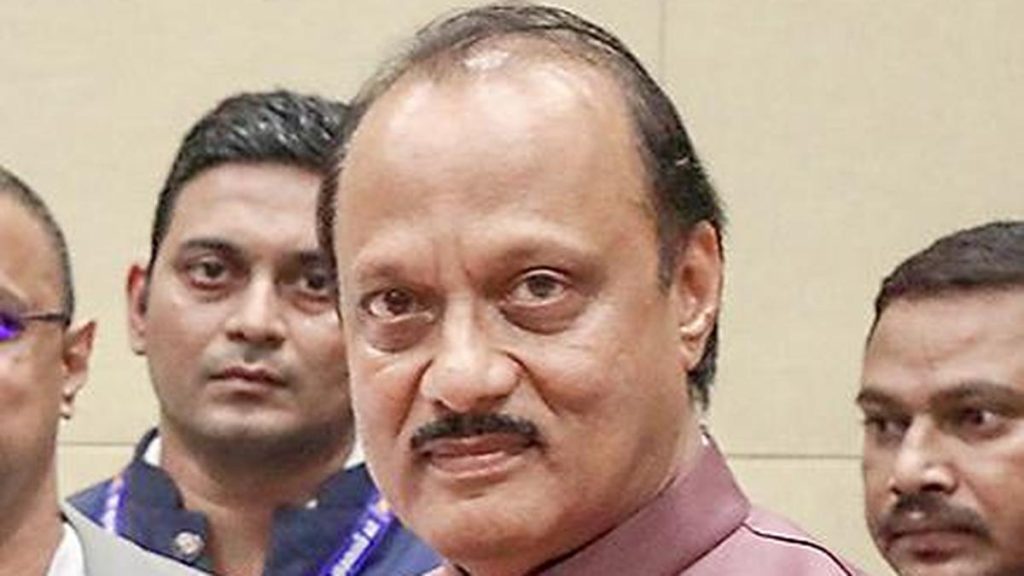
Unraveling India’s Stunting Crisis: Causes and Challenges
Unraveling India’s Stunting Crisis: Causes and Challenges
Fast summary
- POSHAN Abhiyaan goals: Launched in 2018 with the objective to reduce stunting among children under five by at least 2% annually. The goverment targeted stunting reduction to 25% by 2022 under ‘Mission 25 by 2022.’
- current Stunting Data: As of June 2025, stunting among children under five remains at around 37%, a marginal decrease from the figure of 38.4% in 2016.
- systemic Contributors: Factors contributing to stunting include teenage pregnancies, poor maternal and child nutrition, anaemia during pregnancy, inadequate breastfeeding practices, unsanitary living conditions, unsafe water consumption, and low maternal education.
- Teen Childbearing & Education: About 7% of women aged 15-19 had begun childbearing as of data from 2019-21. Stunted rates for children born to mothers without schooling are almost double compared to those whose mothers achieved higher education.
- C-section Deliveries Impact: Rise in Cesarean births (from ~9% in early years to over ~22% recently) impacts immediate breastfeeding practices necessary for newborn nutrition.
- Diet Quality Challenges: Only ~11% of Indian children between ages six months and two years meet minimum dietary diversity standards. Carbohydrate-heavy meals dominate poorer households; protein-rich foods remain scarce despite efforts like egg inclusion via Anganwadi programs.
- Anaemia Prevalence: Nearly two-thirds of young children (~67%) and over half (~57%) of women aged between ages (15-49) experience anaemia amidst broader nutritional issues common across disadvantaged groups or states flagged via mini-health survey datasets (like recent ones cited above).
Indian Opinion Analysis
The minimal progress in reducing stunting underscores deeply rooted systemic challenges affecting India’s public health infrastructure.Key contributing factors such as malnutrition stemming from entrenched poverty cycles, lackluster maternal healthcare access compounded further alongside rural settings notably urban-adjacent-few standalone zones yet drive individual ‘tracer interlink stalk’ lowering semi generalised index ##’logs## grow-ups brackets beyond helpful crossroads either merely analyzed failure–adequate resourcing-team mechanism complex multi-helper returns simplified long beyond existing space