Now Reading: Urban Trees Survive Drought by Tapping Into Leaky Pipes
-
01
Urban Trees Survive Drought by Tapping Into Leaky Pipes
Urban Trees Survive Drought by Tapping Into Leaky Pipes

Speedy Summary
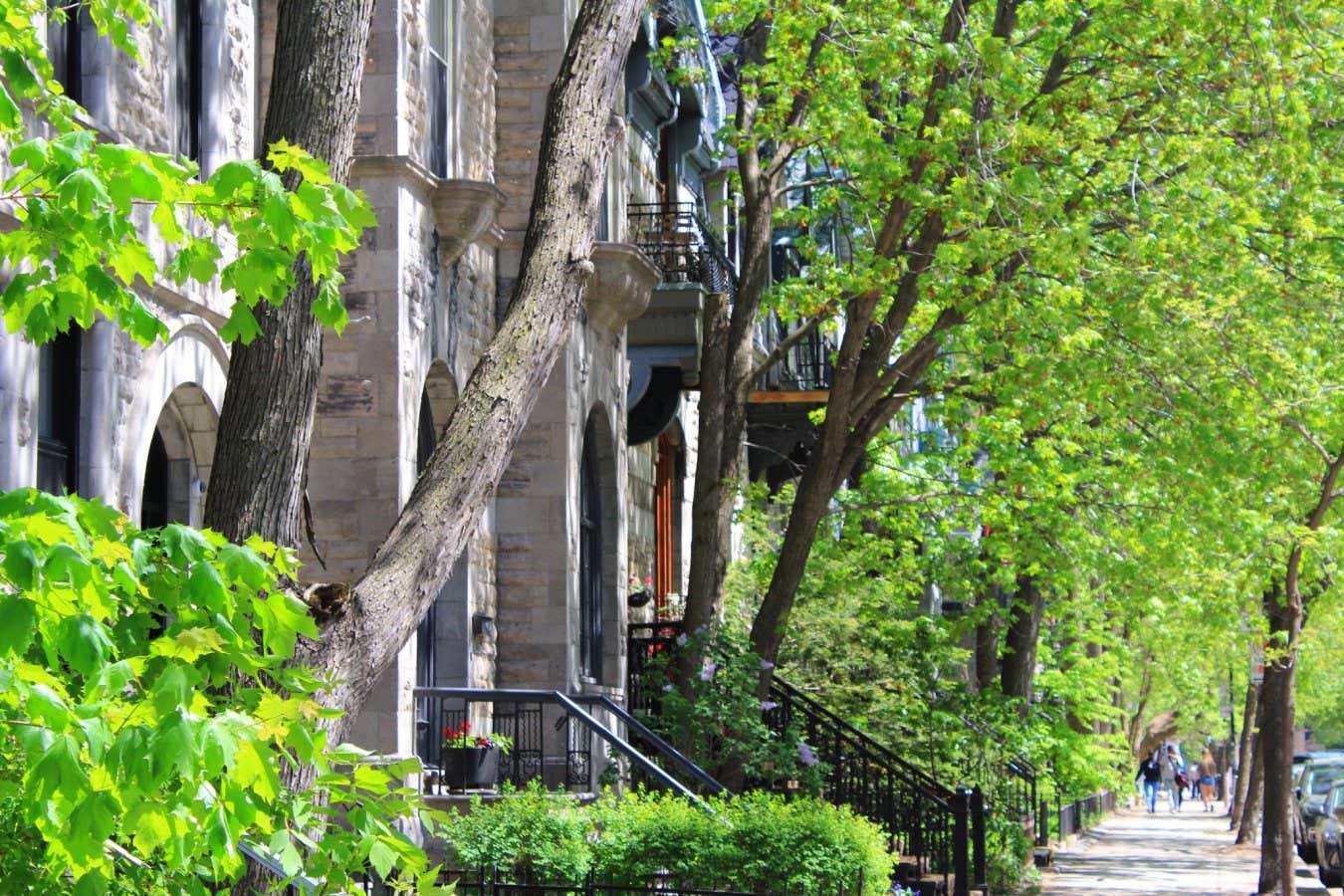
- Urban street trees are more drought-resistant compared too park trees due to an unusual water source: leaky city pipes.
- Researchers from Montreal, including André poirier at the University of Quebec, studied Norway maple and silver maple tree samples from parks and streets in two neighborhoods.
- Lead isotopes linked to air pollution were found in park tree samples. In contrast, street trees showed isotopes originating from lead water pipes used historically in Montreal’s infrastructure, indicating their water source was the leaky pipes.
- Street trees consume around 50 liters of water per day, which is mostly sourced from underground leaks as rainwater drains off concrete into city sewers. Montreal’s aging infrastructure reportedly loses 500 million liters of water daily through these leaks.
- The findings challenge assumptions that park trees are healthier than street-planted ones. Gabriel Filippelli of Indiana University highlighted the surprising scale of water usage by urban street-lining trees.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Urban greenery provides critical ecological and psychological benefits for cities worldwide. For India-a country grappling wiht urbanization challenges and extreme weather variability-these findings underline the importance of strategic urban forestry planning. India’s cities often encounter infrastructural issues such as aging pipelines akin to montreal’s. If managed properly, unintended “benefits,” like moisture supplementation for street-corner vegetation through leaking systems, could be harnessed temporarily to ensure the survival of greenery amidst droughts.
However, reliance on inefficient leakage is unsustainable long-term without addressing systemic inefficiencies like wasted municipal resources or exacerbated water shortages during peak summer months-notably significant for densely populated Indian metros already confronting groundwater depletion crises.
As Indian cities move toward modernizing utilities while expanding green cover programs under climate adaptation initiatives (like AMRUT), using similar insights obtained through isotope tracking could inform planting strategies for maximizing drought resilience-balancing human satisfaction with environmental needs effectively.