Now Reading: Wax Moth Caterpillars Found to Break Down Plastics and Store Them as Fat: Study
-
01
Wax Moth Caterpillars Found to Break Down Plastics and Store Them as Fat: Study
Wax Moth Caterpillars Found to Break Down Plastics and Store Them as Fat: Study
Quick Summary:
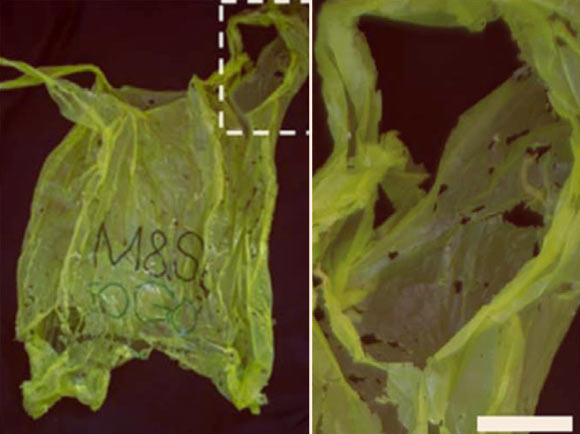
- Scientists have discovered that the caterpillar larvae of the greater wax moth (wax worms) can consume and degrade polyethylene, a widely-used plastic.
- Polyethylene is chemically resilient and can take decades or centuries to fully decompose, with over 100 million tons produced globally each year.
- About 2,000 wax worms can degrade a single polyethylene bag in just 24 hours when supplemented with feeding stimulants like sugars.
- Wax worms do not survive well on a plastic-onyl diet; they lose mass rapidly and die within days. Co-supplementation is being explored to improve their survival during biodegradation efforts.
- two potential solutions identified by scientists include mass rearing wax worms on co-supplemented polyethylene diets for circular economies or re-engineering the biodegradation process outside the insect.
- Wax worm biomass could also be used as nutritious feed for aquaculture fish farming,representing an additional economic benefit.
Image:
!Polyethylene degradation by wax worms
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India faces significant challenges related to plastic pollution, with vast quantities of polyethylene contributing heavily to environmental degradation. The discovery that plastivore insects like wax worms can break down this material offers promising avenues for tackling this global issue. While large-scale implementation using either live larvae or engineered plastic-decomposition mechanisms remains complex, such innovations could complement India’s burgeoning focus on sustainable and circular economies.
Further research into microbial contributions within these organisms may offer new opportunities for biotechnological applications in India’s industrial ecosystems. However, reliance solely on natural processes like wax worm consumption must be approached cautiously-given their reduced fitness levels during decomposition-ensuring ethical treatment of organisms paired with practical scalability objectives.
The potential use of insect biomass as aquaculture feed aligns well with India’s fisheries sector expansion plans but would require detailed regulatory frameworks considering biosafety implications. coupling biological solutions with existing waste management systems might propel India toward more effective strategies against its mounting plastic waste crisis.