Now Reading: What Determines the Shapes of Clouds?
-
01
What Determines the Shapes of Clouds?
What Determines the Shapes of Clouds?
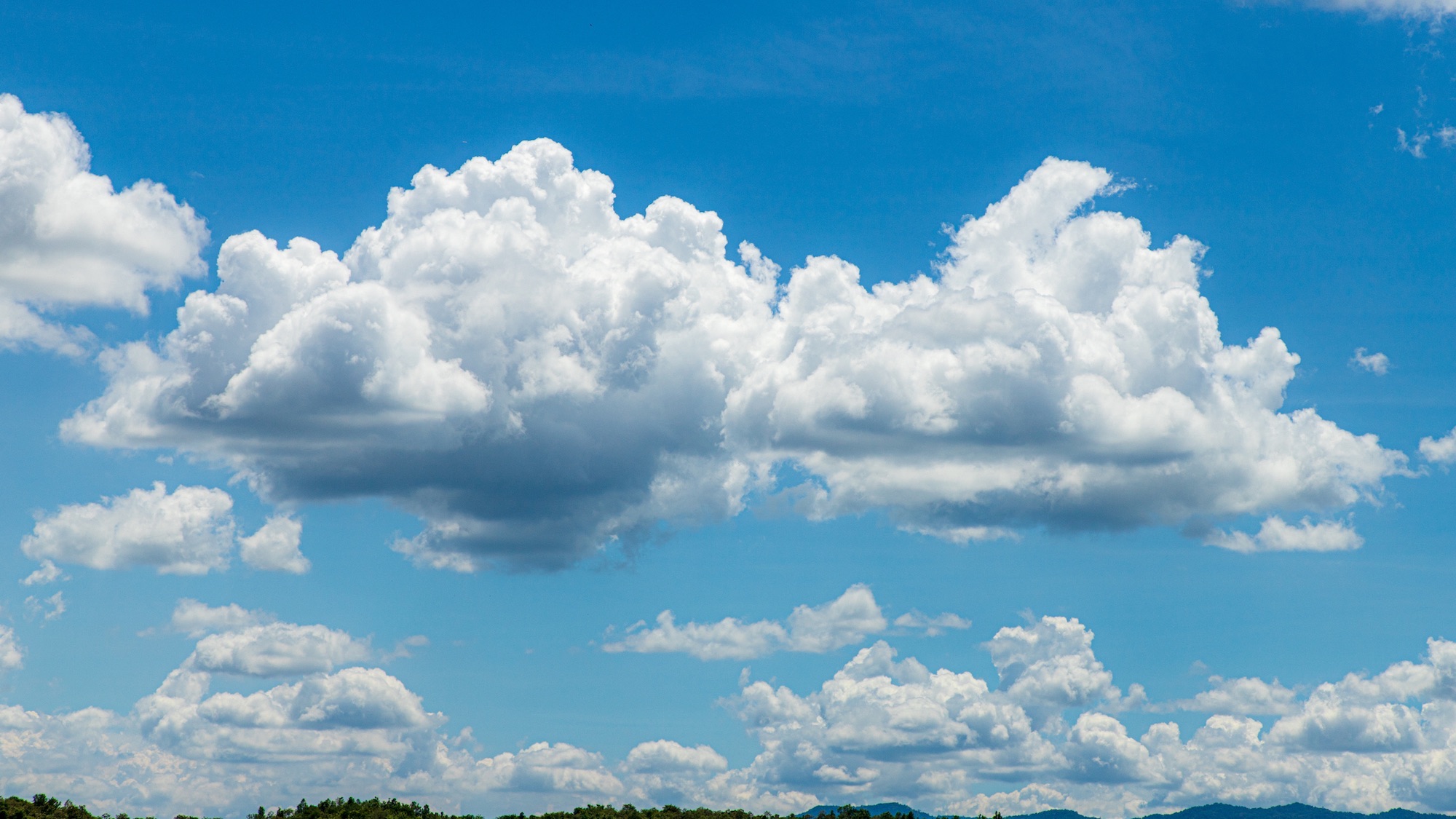

Fast summary
- Cloud Formation Basics: clouds form when air rises, cools, and water vapor condenses into droplets or ice crystals.
- Types of Clouds: Scientists classify clouds into ten main types based on their shape and altitude,ranging from cumulus (cotton-like) to cirrus (feathery).
- Composition & Appearance: Low-altitude clouds primarily consist of water droplets with crisp edges, whereas high-altitude clouds are mainly ice crystals with translucent appearances.
- Impact of Air Movement: Processes such as convection influence cloud shapes; as an example, warm air rising rapidly can create towering cumulonimbus clouds associated with thunderstorms.
- Role of Winds & Topography: High-altitude winds shape cirrus clouds into delicate strands; mountain ranges cause lenticular cloud formations resembling flying saucers.
- Meteorological Significance: Cloud shapes provide critical clues for weather forecasting.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Understanding the science behind cloud formation and shapes offers valuable insights that go beyond meteorology. while these observations may seem abstract in the Indian context,they hold practical implications for agriculture-dependent regions where weather predictions are crucial for planning crop cycles. IndiaS diverse topography-with its mountains and plains-creates unique atmospheric conditions conducive to various cloud formations that can influence regional rainfall patterns. Investing in meteorological research informed by global scientific advancements like this could further bolster India’s preparedness against extreme weather events such as monsoon storms or heatwaves.