Now Reading: Why Combining In Vivo and In Vitro Trials Yields Better Results
-
01
Why Combining In Vivo and In Vitro Trials Yields Better Results
Why Combining In Vivo and In Vitro Trials Yields Better Results

Swift Summary
- Definition:
– In vivo studies are conducted within living organisms, such as lab animals or humans, and help test biological processes in a natural habitat.
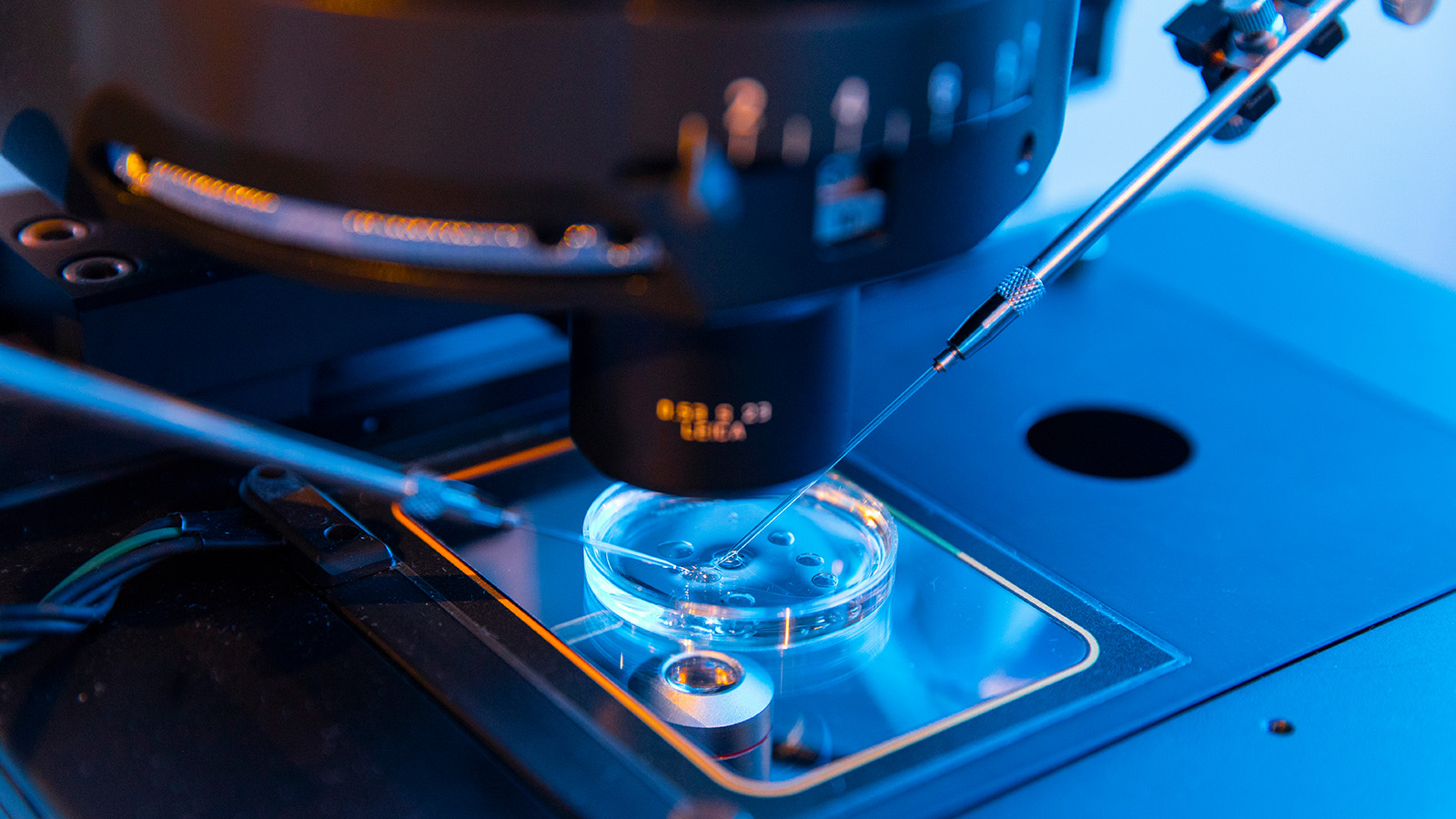
– In vitro studies occur outside living organisms in controlled environments like test tubes or petri dishes, allowing for precision at the cellular level.
- Strengths and Weaknesses:
– in vitro: Cost-effective, scalable, and yields quick results but lacks systemic interactions found in whole organisms.
– In vivo: Offers realistic insight into complex systems but is more expensive and time-consuming.
- Applications: Common uses include IVF (in vitro fertilization), drug screening using cell models (in vitro), measuring immune responses (in vivo), or studying disease progression.
- Research Process: Medical research frequently enough progresses from in vitro tests (hypothesis refinement) to in vivo trials (validation within biological systems) before human clinical trials under strict ethical protocols.
- Integration of Both Methods: the gold standard combines both approaches-initial exploratory experiments in controlled settings followed by validation in living systems-ensuring complete insights.
Indian opinion Analysis
The exploration of in vivo vs. in vitro methods illustrates their complementary roles in advancing scientific data collection globally as well as their applications across industries like medicine and drug growth. For India, wich is prioritizing high-quality biotech innovation under various “Make in India” initiatives, mastering these methodologies can bridge gaps between early-stage experimentation and clinical solutions ready for market use.
India’s burgeoning pharmaceutical sector stands to benefit significantly from integrating precise automated processes such as controlled-vitro frameworks while ensuring compliance via robust pre-human-trial-centered mechanisms advocated internationally this topic builds future policy contexts though nuanced debates !
Read more