Now Reading: Why Flu Becomes Deadly for Seniors: Scientists Uncover Key Cause
-
01
Why Flu Becomes Deadly for Seniors: Scientists Uncover Key Cause
Why Flu Becomes Deadly for Seniors: Scientists Uncover Key Cause

speedy Summary
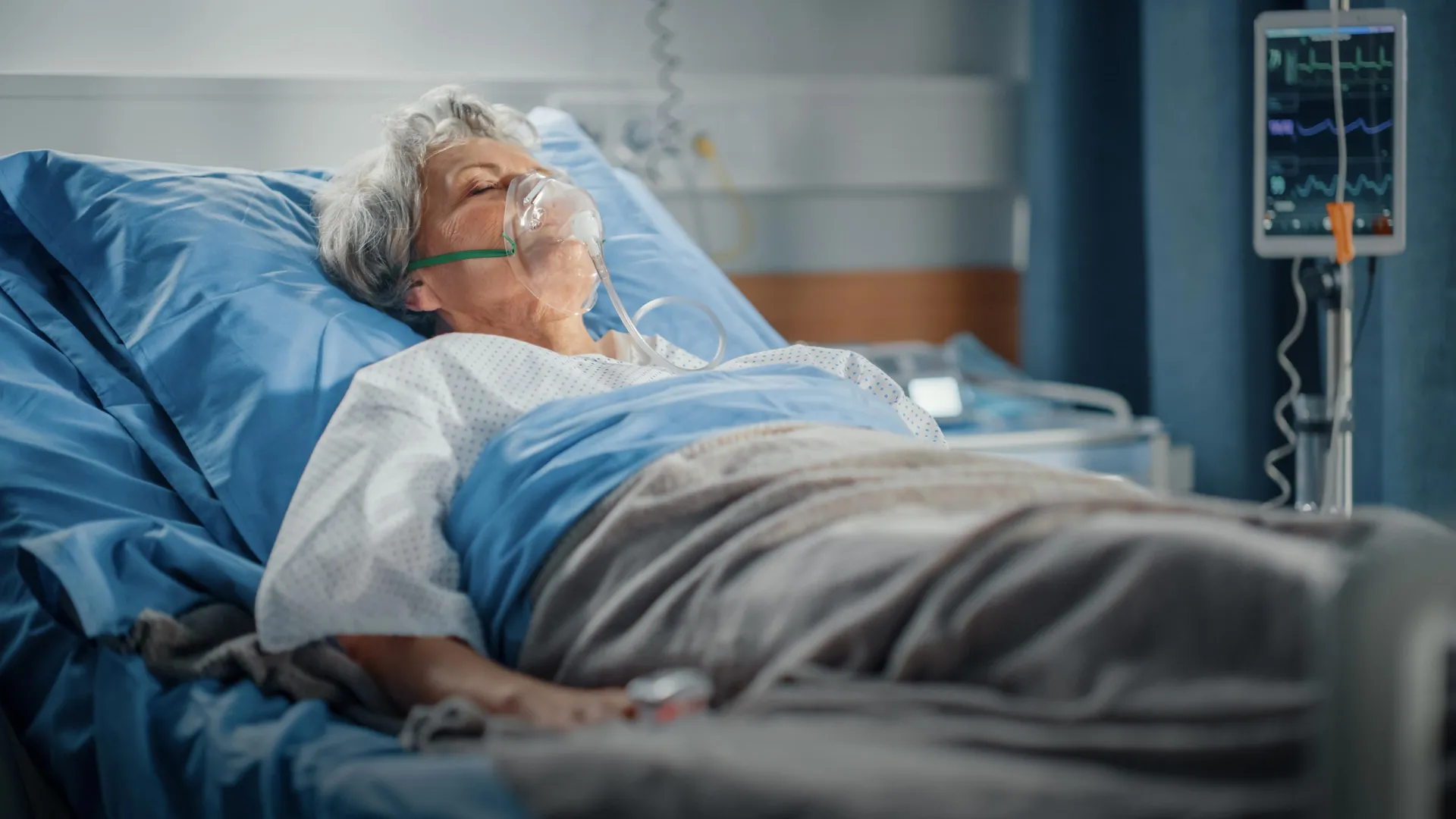
- Scientists discovered why older individuals are more prone to severe influenza infections.
- Higher production of a protein called Apolipoprotein D (ApoD), associated with lipid metabolism and inflammation, was identified in aging lungs.
- Elevated ApoD levels lead to reduced antiviral type I interferon response and notable lung tissue damage during infection.
- Extensive breakdown of mitochondria due to ApoD impairs immune system activation, increasing virus replication and severity of disease outcomes.
- The study used an aging-mouse model and human tissue samples for examination.
- ApoD is now recognized as a potential therapeutic target to mitigate severe influenza effects in the elderly population.
- Researchers highlight the urgent need for intervention as global aging trends pose challenges for healthcare systems and economic resources.
Image: (No images specified in source)
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research presents vital insights into age-related vulnerabilities during influenza infections, emphasizing the role of ApoD as a key mediator. For India, where healthcare access varies widely across demographics, such findings hold meaning. With an expanding aged population projected over coming decades, this advancement could pave pathways toward targeted treatments that meet India’s unique public health needs. By investing early into therapeutic advancements derived from studies like this one, it becomes possible not only to reduce mortality rates but also alleviate economic strain linked to prolonged healthcare demands on senior citizens.Moreover, awareness campaigns about age-specific risk factors related to infectious diseases may help India prioritize preventive care initiatives across regions disproportionately affected by aging populations. Neutralizing proteins like ApoD might open doors for personalized medicine compatible with India’s diverse genetic composition-a consideration pivotal given it’s scale within global elderly demographic projections.