Now Reading: Wi-Fi 8 Aims to Eliminate Dead Spots, Shifting Focus from Speed
-
01
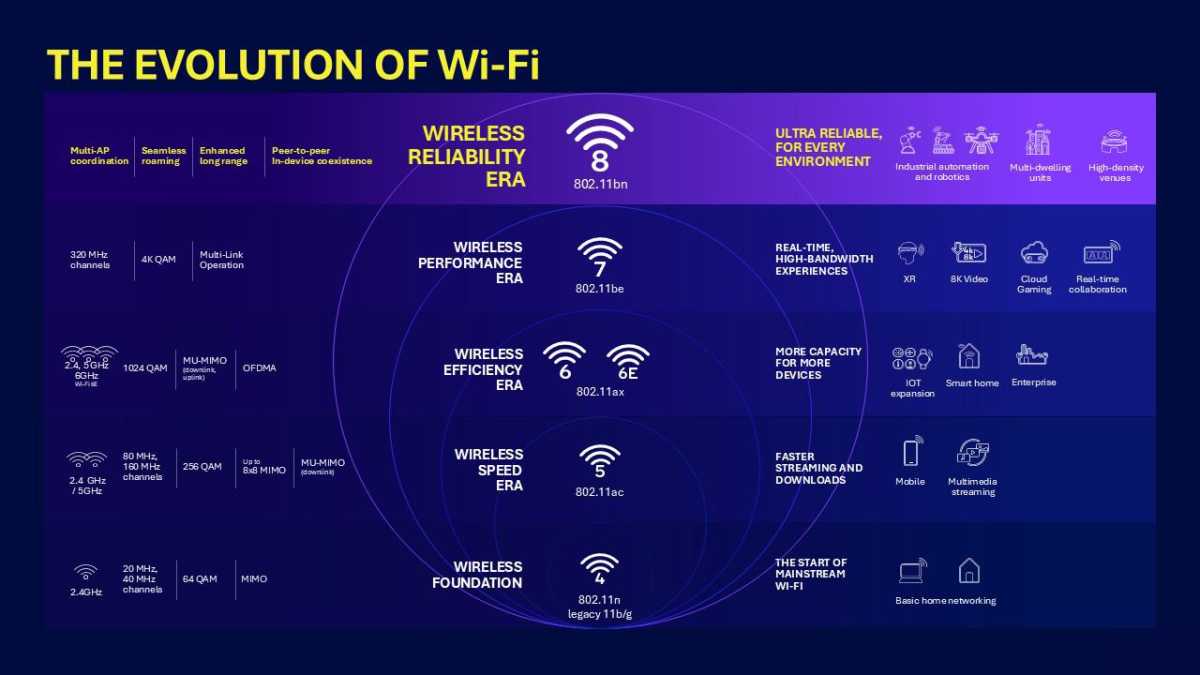
Wi-Fi 8 Aims to Eliminate Dead Spots, Shifting Focus from Speed
Wi-Fi 8 Aims to Eliminate Dead Spots, Shifting Focus from Speed

Speedy Summary:
- Wi-Fi 8, based on the IEEE’s draft 802.11bn standard, is in advancement with a focus on reliability rather than faster speeds.
- Key advancements include:
– Single Mobility Domains: Seamless low-latency roaming between access points.
– Edge Reliability: Improved stability for connections at the edge of range.
– Cooperative Behavior: Dynamic adjustments to handle dense environments like stadiums and conference centers.- Compatibility Management: Better coordination between Wi-Fi,Bluetooth,NFC,and other wireless technologies within devices.
– Power Efficiency: Enhanced mechanisms for optimizing energy consumption without degrading connection quality.
- Qualcomm has promoted this new standard and is expected to integrate it into its chipsets quickly.
- Devices will need new hardware to support Wi-Fi 8 but will share similarities with Wi-Fi 7 equipment due to overlapping frequency bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz).
- Apple’s adoption of Wi-Fi standards tends to follow formal approval. Current projections suggest consumer availability around 2028, coinciding with Apple’s shift to proprietary chips for wireless technologies.

Indian Opinion Analysis:
The development of Wi-Fi 8 underscores a global shift in networking priorities from raw speed toward enhanced reliability-a move highly relevant for India given its massive population and expanding digital infrastructure needs. As India continues embracing IoT-driven technologies across sectors like education, healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities through projects like Digital India Mission or BharatNet initiative-reliable connectivity becomes paramount over maximum throughput speeds.
Features such as seamless mobility domains could greatly benefit India’s large public venues (e.g., railway stations and stadiums), reducing user frustration caused by network interruptions during handovers between access points. Similarly improved edge reliability aligns well with rural connectivity challenges where network signals often degrade due longer physical separation same applies needed relevance behind inter R&D scope tight-energy costs alternative devices architect implementations household scales limited budget user patterns etc..
Read More