Now Reading: X-ray and Radio Unite in Striking New Image
-
01
X-ray and Radio Unite in Striking New Image
X-ray and Radio Unite in Striking New Image

Quick Summary
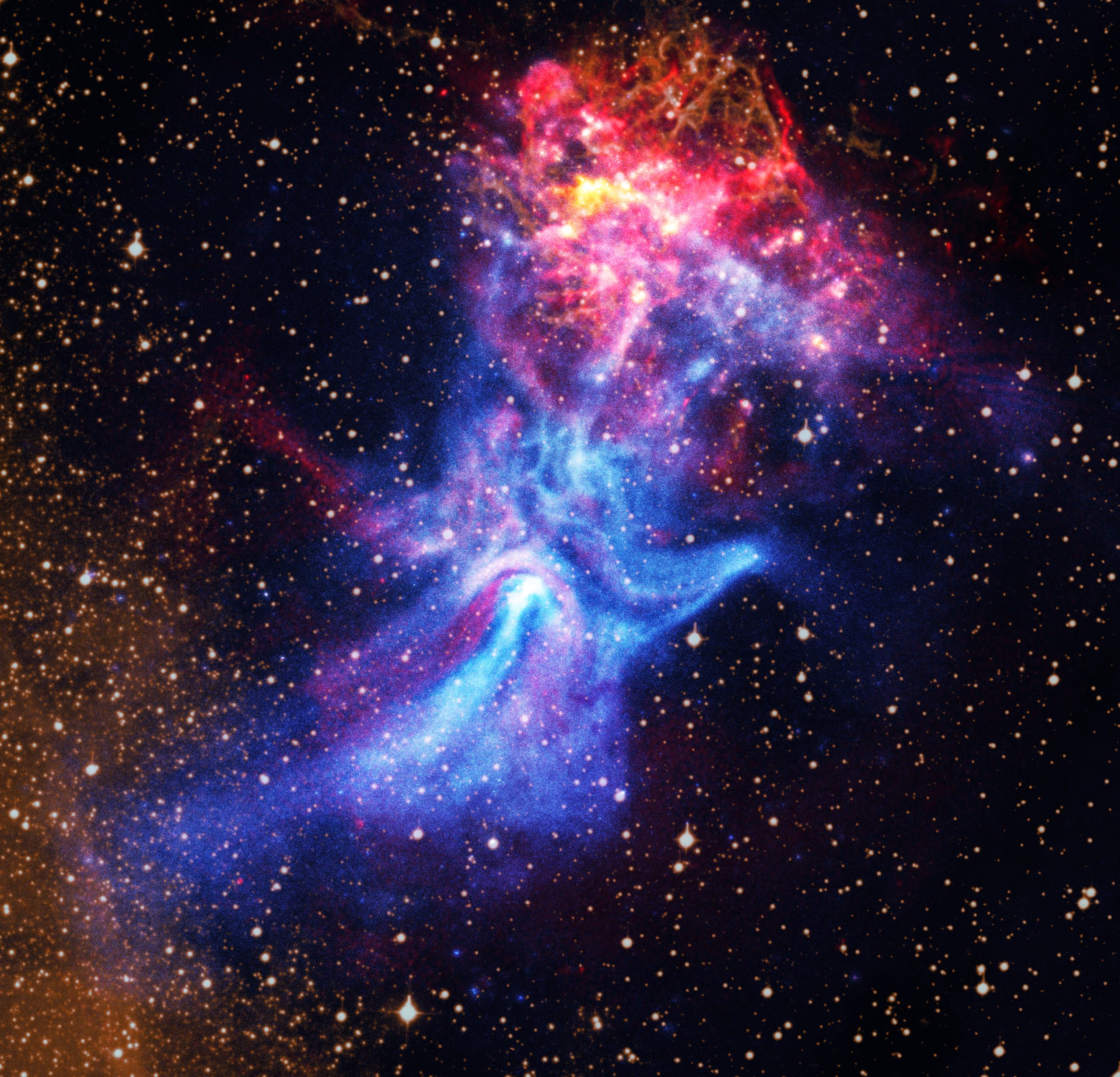
- Discovery Details: NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory captured a nebula shaped like a hand, surrounding pulsar B1509-58, a rapidly spinning neutron star (12 miles in diameter).
- New Insights: combined radio data from the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) and Chandra X-ray data reveal intricate details about the nebula (MSH 15-52) and supernova remnant RCW 89.
- Nebula Features: The nebula spans over 150 light-years; high-energy particles drive its “fingers” that overlap magnetic field lines. its resemblance to a cosmic hand is striking in composite images of X-ray, radio, and optical data.
- Supernova Remnant Observations: Radio emissions show patchy alignment with hydrogen clouds; differences are noted between X-rays and radio waves at certain features.
- Scientific Challenges: Researchers identified areas where emissions behave unexpectedly – such as sharp contrasts in boundaries and the lack of corresponding signals between different wavelengths.
- Implications for Astrophysics: Detailed study suggests complex interactions between pulsar winds and supernova debris but leaves many unanswered questions about the mechanisms behind these phenomena.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The collaborative use of diverse observational tools-like ATCA’s radio data combined with NASA’s Chandra X-ray imagery-not only highlights advanced astrophysical research but also underscores significant international cooperation in space exploration. This discovery serves as another reminder of humanity’s pursuit to understand cosmic phenomena through persistence and innovation. While immediate links to india may not be evident,advancements like these directly contribute to foundational scientific knowledge which increasingly supports global spaces for emerging nations like India to participate more actively.
India’s space programs have shown growing ambition through projects such as Chandrayaan mission series aimed at lunar exploration. expanding local expertise into observational astronomy or collaborating internationally could elevate India’s capacity within this domain while enriching its broader contributions toward understanding celestial mechanics on rare scales-a vision relevant both nationally and scientifically.